Unearned revenue is not an uncommon liability; it can be seen on the balance sheet of many companies. Unearned revenue or deferred revenue is considered a liability in a business, as it is a debt owed to customers. It is classified as a current liability until the goods or services have been delivered to the customer, after which it must be converted into revenue. Unearned revenue refers to the money small businesses collect from customers for a or service that has not yet been provided. In simple terms, unearned revenue is the prepaid revenue from a customer to a business for goods or services that will be supplied https://www.bookstime.com/ in the future. On January 1st, to recognize the increase in your cash position, you debit your cash account $300 while crediting your unearned revenue account to show that you owe your client the services.
- Once a delivery has been completed and your business has finally provided prepaid goods or services to your customer, unearned revenue can be converted into revenue on your balance sheet.
- When a company records unearned revenue, it does so as a liability on its balance sheet.
- Companies must ensure transparency in their financial statements by correctly reporting unearned revenue according to accounting standards.
- After you provide the products or services, you will adjust the journal entry once you recognize the money.
- A publishing company may offer a yearly subscription of monthly issues for $120.
- Unearned service revenue is considered a liability because the company has an obligation to perform services for the amount it collected in advance.
Where does unearned (prepaid) revenue go on a balance sheet?

Since service is owed, it is considered a short-term or long-term liability. Once revenue recognition occurs, it is earned revenue and becomes income. The adjusting entry for unearned revenue will depend upon the original journal entry, whether it was recorded using the liability method or income method. A business owner can utilize unearned revenue for accounting purposes to accurately reflect the financial health of the business. This type of revenue, for one, provides an opportunity to help small businesses with cash flow and working capital to keep operations running and produce goods or provide services.

What Are Some Common Examples of Current Liabilities?
The balance of the money paid early will remain in the unearned revenue account and should only be recognized as the goods and services are provided each month. Unearned revenue is most common among companies selling subscription-based products or other services that require prepayments. Classic examples include rent payments made in advance, prepaid insurance, legal retainers, airline tickets, prepayment for newspaper subscriptions, and annual prepayment for the use of software. It’s categorized as a current liability on a business’s balance sheet, a common financial statement in accounting. And so, unearned revenue should not be included as income yet; rather, it is recorded as a liability.
What is the Definition of Deferred Revenue?
- Advances from customers can be initially recorded as Unearned Service Revenue (a liability) or Service Revenue (income).
- The accounts will then be adjusted later when the services are rendered or at the end of the accounting period by preparing adjusting entries.
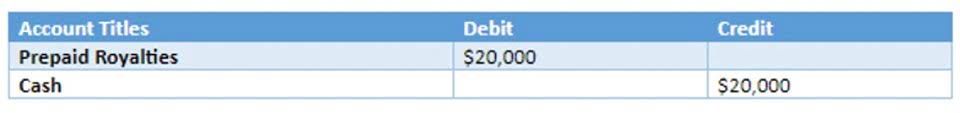
- Upon receipt of the payment, the company’s accountant records a debit entry to the cash and cash equivalent account and a credit entry to the deferred revenue account for $1,200.
- Later, you will make the necessary adjusting journal entries once you recognize part of or the entire prepaid revenue amount.
- It would go in the “liabilities” category, as it is money owing.
- Unearned revenue can provide clues into future revenue, although investors should note the balance change could be due to a change in the business.
Unearned revenue can be rent payments that are received in advance, prepayments received for newspaper subscriptions, annual prepayments received for the use of software, and prepaid insurance. The payment is considered a liability to the company because there’s a possibility that the good or service may not be delivered or the buyer might cancel the order. Deferred revenue is a liability because it reflects revenue that hasn’t yet been earned and it represents products or services that are owed to a customer. It’s recognized proportionally as revenue on the income statement as the product or service is delivered over time.
- The company would have to repay the customer in either case unless other payment terms were explicitly stated in a signed contract.
- However, a business owner must ensure the timely delivery of products to its consumers to keep transactions steady and drive customer retention.
- At the end every accounting period, unearned revenues must be checked and adjusted if necessary.
- Short-term debt is typically the total of debt payments owed within the next year.
- Accounting standards according to GAAP, or Generally Accepted Accounting Principles, allow for different methods of revenue recognition depending on the circumstances and the company’s industry.
- If the delivery date is extended beyond 12 months after the transfer of the revenue, then it will be recorded under long-term liability.
Unearned Service Revenue
In addition, property management companies, insurance companies, and other companies that require an advance payment frequently need to record unearned revenue. The revenue recognition principle dictates that revenue should be recognized when it is is unearned revenue a current liability earned, regardless of when payment is received. This principle ensures accurate reflection of a company’s financial performance on its financial statements, allowing stakeholders to make informed decisions. Say a company has a balance of unearned revenue for services it intends to provide within a year, this balance is considered a current liability and would decrease the working capital. Short-term debts can include short-term bank loans used to boost the company’s capital. Overdraft credit lines for bank accounts and other short-term advances from a financial institution might be recorded as separate line items, but are short-term debts.

Adjusting journal entries

The first journal entry reflects that the business has received the cash it has earned on credit. Other names used for this liability include unearned income, prepaid revenue, deferred revenue and customers’ deposits. Unearned revenue and deferred revenue are interchangeable terms. Both refer to payments received for products or services to be delivered in the future. These payments are recorded as liabilities until the goods or services are provided, at which point they are recognized as revenue. In summary, unearned revenue is a vital concept within accrual accounting, helping provide a more accurate representation of a company’s financial position.
The liability https://x.com/BooksTimeInc is reduced as the company fulfills its obligations, and the revenue is recognized in the income statement. By understanding and properly accounting for unearned revenue, businesses can maintain accurate financial records and ensure that their financial statements reflect their true financial position. Properly managing unearned revenue is crucial for industries such as software or subscription-based services where prepayments are the norm. Various adjustments and corrections may also be required as the company continues to provide the goods or services it has received payment for and gradually “earns” the revenue. This is money paid to a business in advance, before it actually provides goods or services to a client.


 by
by